Opioids are commonly prescribed to treat chronic pain. Unfortunately, this can easily lead to abuse and addiction. While in treatment, alternative methods will be used to treat the pain and the substance use disorder.
Chronic Pain Management & Drug Addiction Treatment
Chronic pain-related conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lower back pain and hip bursitis often require long-term treatment regimens involving opiate pain-relieving drugs. According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, an estimated 116 million Americans live with chronic pain conditions within any given year.
Considering the high addiction potential opiate drugs carry, it’s no surprise that many entering addiction treatment also suffer from pain-related conditions. Unlike people just dealing with addiction issues, people affected by chronic pain symptoms still require some form of pain management therapy when being treated for opiate addiction.
Fortunately, addiction treatment programs can take steps to provide for a person’s pain management needs while helping him or her overcome opiate addiction.
Opiates: The Magic Bullet for Chronic Pain
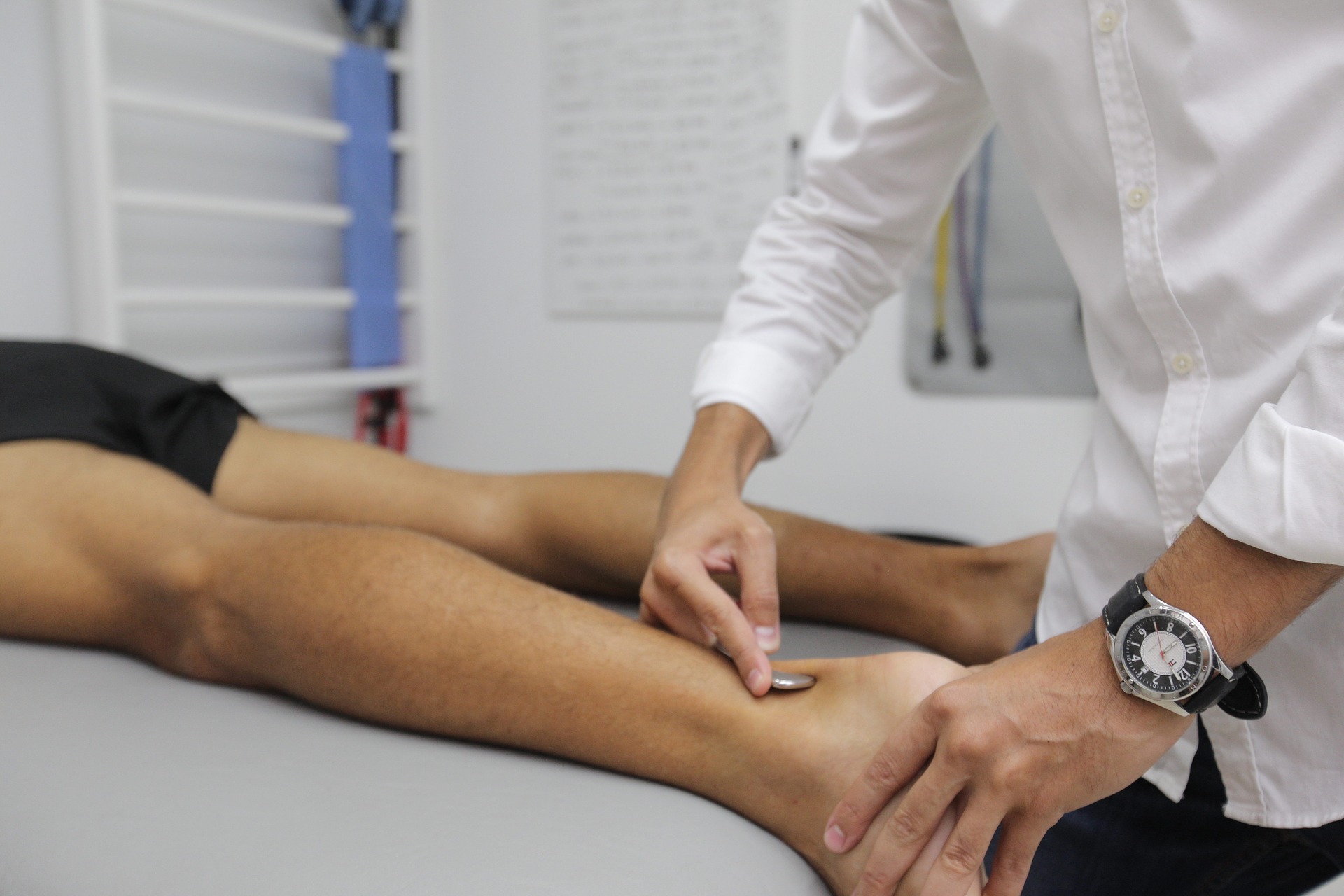
When detoxing from prescription medication, it’s important to find an alternative therapy to manage your pain.
Opiate-based prescription pain medications offer the most effective means for treating pain symptoms of most every kind and remain the standard of care, worldwide, according to the U. S. National Library of Medicine. As a group, opiates work by preventing pain signals from reaching the sensory processing areas of the brain.
With each drug dose, opiates trigger the release of endorphins, the body’s own natural “feel good” chemicals. While effective, over time, these effects disrupt the brain’s chemical system to the point where essential brain functions become dependent on the drug’s effects.
Effects of Long-Term Opiate Use
The long-term effects of opiate use create a state of physical and psychological dependency. Psychological dependence takes root within a person’s thinking, emotions and belief systems and lies at the heart of addiction.
Long-term opiate use also weakens the brain and body’s responsiveness to the drug. When this happens, a person’s pain symptoms can actually worsen with continued drug use. In effect, pain management and addiction treatment both become top priorities after so many months or years of opiate use. You can learn more about treatment options by calling 800-934-1582(Sponsored) .
Treating Addiction & Chronic Pain Together
Thorough Assessment
As detox marks the first stage of addiction treatment, the absence of opiates not only brings on severe withdrawal effects but also leaves chronic pain symptoms untreated. Pain symptoms can greatly aggravate the withdrawal process so finding an effective pain management approach becomes paramount during the early stages of addiction treatment.
In order to do this, treatment programs conduct a thorough assessment to determine what course of pain management therapy will work best. The assessment process covers a range of areas, including:
- Length of time using opiates
- Family history of substance abuse
- Mental health history
- Duration of pain-related condition
- Lab testing, such as urine and blood testing
Pain Management Plan
Many who take opiates to treat chronic pain fall into an anxiety-ridden cycle where feelings of anxiety develop in anticipation of pain symptoms. This cycle, in and of itself, poses its own set of problems for both pain management and addiction treatment purposes. A pain management plan identifies the risks as well as the benefits of any one course of pain treatment as well as how it fits in with a person’s overall course of addiction treatment.
Pain Management Treatment Options
Pain management treatment options run the gamut in terms of the different types of approaches available, some of which include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents
- Biofeedback techniques
- Hypnosis
- Physical therapy
More often than not, pain symptoms stem from both physical and psychological components, so treatment programs also employ behavioral approaches to help manage pain symptoms. Behavioral interventions may take the form of group therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy and/or support group work.
Considerations
In spite of the widespread use of prescription opiate medications for pain management purposes, these drugs carry an incredibly high risk for abuse and addiction. Anyone who struggles with addiction issues as a result of long-term opiate use may want to seriously consider getting needed treatment help. You can start the treatment process today by calling 800-934-1582(Sponsored) .
the Take-Away

